Call Us
310-274-4401
Skin Cancer
What Is Skin Cancer?

What Is Basal Cell Carcinoma?
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer in the United States. The skin lesions often develop on sun-exposed skin, including the face, ears, scalp, chest, and back. Basal cell carcinoma may appear as a pink, translucent papule. They can be bright pink and can bleed easily.
Following a biopsy, a confirmed basal cell carcinoma can be treated by excising it surgically, spraying it with liquid nitrogen (cryotherapy), and even treating it simply with targeted creams that interfere with the cancer cell growth.
Key risk factors for basal cell carcinoma include:
- Excessive sun exposure, including tanning beds
- Fair skin
- Age
- Family history of skin cancer
- Weakened immune system due to either medications or medical conditions

Lasers for Skin Cancer Prevention
What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma?
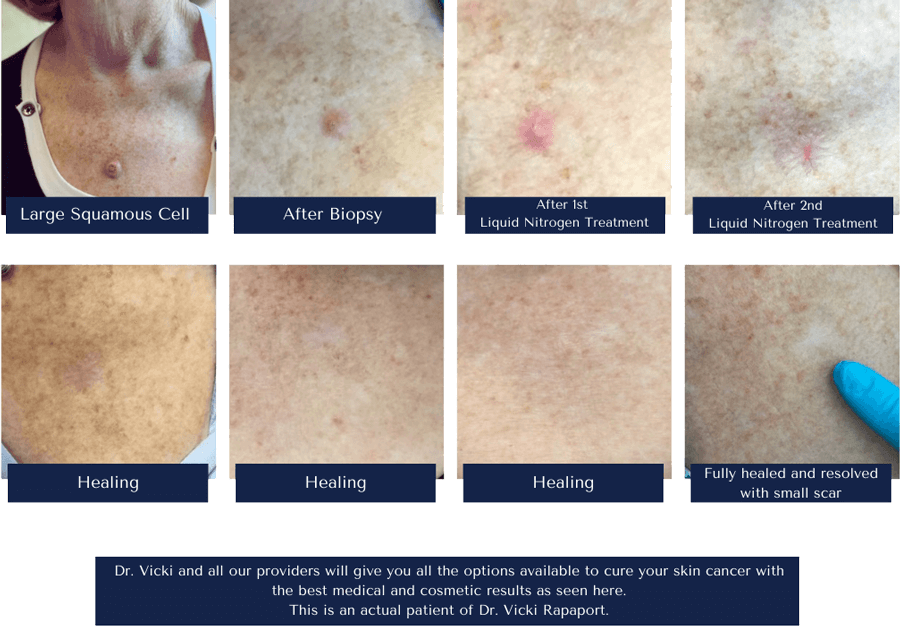
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common type of skin cancer. These tumors usually develop in sun-exposed areas of your skin, including the face, scalp, ears, hands, and neck. Unfortunately, squamous cell carcinoma may also develop on other areas of your body not exposed to the sun.
Squamous cell carcinoma may appear as a wart-like growth, an open bleeding sore, or a scaly patch that does not resolve.
A biopsy is needed to confirm the presence of a squamous cell carcinoma. Treatment may depend on the location, size, and depth of the lesion. Surgical excision is the primary method of treatment, but there are many other methods for removing these lesions, including:
- Cryotherapy
- Curettage and Electrodessication
- Targeted Topical Creams
A general rule of thumb is to get a skin check at minimum once a year to find these lesions at their earliest stages.
What Is Melanoma?
Malignant melanoma is the most concerning of all of the skin cancers. The main signs and symptoms of this skin cancer include these changes:
- Asymmetry
- Border irregularity
- Color variation
- Diameter larger than 6mm
- Evolving (changes over time)
If your provider suspects your skin growth is melanoma, they will take a biopsy and have it reviewed by a pathologist. When detected early, melanoma can be cured. If your melanoma is advanced, you may require more extensive surgery, along with radiation, chemotherapy, and/or immunotherapy.
Early detection is critical. It is important to monitor your skin throughout the year and visit your provider regularly.